Technology
The Risks of AI: Job Displacement, New Opportunities, and Skill Requirements
Published
3 years agoon

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a topic of great interest in recent years, with many believing it can revolutionize the way we work and live. However, there are growing concerns about the impact it may have on jobs and society as a whole. In this article, we will explore the potential and risks of AI and its impact on the workforce.
The Power of AI
AI has the power to enhance productivity and transform many sectors of the economy. Its ability to automate tasks and processes that were previously performed by humans can free up time and resources for more complex and creative work.
For example, AI chatbots can summarize customer complaints and respond to them quickly, which can save businesses time and money. AI can also improve the quality of life by providing instant access to information and services through smartphones and other devices.

The Risks of AI
Despite its potential benefits, AI also poses several risks to the workforce and society as a whole. Here are some of the main risks of AI:
- Job Losses: As AI technology becomes more advanced, it may replace jobs that were previously performed by humans, particularly those that are repetitive or low-skilled.
- Skills Gap: As AI technology becomes more prevalent, workers may need to learn new skills to remain competitive in the job market. This may lead to a skills gap that could leave some workers behind.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI algorithms can be biased, which could lead to discrimination against certain groups of people. For example, facial recognition technology has been shown to be less accurate for people with darker skin tones.
- Loss of Privacy: AI technology can collect and analyze vast amounts of data, which raises concerns about privacy and surveillance.

The Impact of AI on the Workforce
The impact of AI on the workforce is complex and depends on many factors. Here are some of the key impacts of AI on the workforce:
- Job Displacement: AI technology has the potential to replace jobs that were previously performed by humans, which could lead to job losses.
- New Job Opportunities: AI technology also creates new job opportunities, particularly in the areas of AI development, data science, and automation.
- Skill Requirements: The rise of AI technology means that workers may need to learn new skills to remain competitive in the job market.
- Workforce Diversity: AI technology can help to improve workforce diversity by removing bias from hiring processes and providing opportunities for underrepresented groups.

Preparing for the Future of Work
To prepare for the future of work in an AI-dominated economy, workers will need to adapt and learn new skills. Here are some strategies for preparing for the future of work:
- Lifelong Learning: Workers will need to continue learning new skills throughout their careers to remain competitive in the job market.
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Employers can help workers to learn new skills by offering training and development opportunities.
- Collaboration between Humans and AI: Humans and AI can work together to achieve better outcomes. Workers can learn to collaborate with AI systems to improve productivity and efficiency.
- Ethical and Responsible AI: Policymakers and society as a whole must ensure the ethical and responsible integration of AI into the workforce to minimize negative impacts on vulnerable groups.
AI has the potential to transform many sectors of the economy and improve the quality of life for many people. However, it also poses risks to jobs and society. To maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing its risks, we must prepare for the future of work by adapting and learning new skills, collaborating with AI systems, and ensuring the ethical and responsible integration of AI into the workforce. With proactive measures, we can harness the power of AI to create a better future for all.
Key Takeaways
- AI has the power to revolutionize industries and enhance productivity, but it also poses risks to jobs and society.
- Job displacement, bias, and privacy concerns are some of the risks associated with the rise of AI.
- AI creates new job opportunities, but workers need to learn new skills to remain competitive in the job market.
- Strategies for preparing for the future of work include lifelong learning, upskilling and reskilling, and collaboration between humans and AI.
- Ensuring the ethical and responsible integration of AI into the workforce is crucial to minimizing negative impacts on vulnerable groups.
You may like
-


Can smart technology unlock a sustainable future?
-

AI’s Journey Through the Heart of Political Change
-

Killer Robots: The New Era of Warfare?
-


Job Security in the Era of Artificial Intelligence
-


The AI Revolution: The Game Changer in Media Coverage
-


How Can We Overcome Our Fears About Artificial Intelligence?
Technology
Unlocking the Power of Smart Devices: What You Need to Know
Published
1 year agoon
August 21, 2024By
Teddy Morgan
In today’s hyper-connected world, the term “smart device” is tossed around frequently, but what exactly does it mean?
A smart device is an electronic gadget that can connect to the internet, gather data from its surroundings, and perform tasks autonomously. Let’s dive into the key characteristics that make a device truly “smart” and explore both the benefits and drawbacks of this technology.
The Three Key Features of a Smart Device
1. Context Awareness
A smart device can understand its environment and adapt its behavior accordingly. This ability, known as context awareness, relies on sensors like cameras, microphones, GPS receivers, radar, and LiDAR. These sensors collect data, which the device uses to make informed decisions. For example, a smart thermostat can detect the current temperature and adjust the heating or cooling system without manual input.
2. Autonomous Computing
Autonomous computing is the capability of a device to perform tasks independently, without requiring direct user commands. Consider your smartphone, which might suggest an umbrella if it detects rain in the forecast. This simple action demonstrates the power of autonomous computing—using context data to make decisions on your behalf.
3. Connectivity
Connectivity is the backbone of a smart device’s functionality. It allows these devices to communicate with each other and the broader Internet of Things (IoT). Whether through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or another wireless connection, smart devices use connectivity to share data and work together seamlessly.
How Do Smart Devices Work?
Smart devices rely on IoT to connect with sensors attached to objects or other networked devices. These sensors gather data, which the smart device can store, analyze, and share with other devices. When multiple smart devices are connected to the same network, they can be managed through a single platform, making it easier to monitor and control them remotely.
Do Smart Devices Need Human Interaction?
Not all smart devices are designed to interact directly with humans. While we often think of smartphones, smart TVs, or smartwatches, many smart devices operate independently of human input. For instance, a weather probe might collect and transmit data without any direct human involvement. Although humans will eventually use this data, the device itself functions autonomously.
Must Smart Devices Be Portable?
Not necessarily. Take a smart surveillance camera, for example. It meets the criteria of a smart device—it’s context-aware (it can recognize objects), autonomously computes (it identifies and reports objects using computer vision), and is connected to a network (it sends data to a server). Portability isn’t a requirement for a device to be smart; what matters is its ability to sense, process, and connect.
Benefits of Smart Devices
Energy Savings: Smart devices can reduce energy consumption by automatically turning off when not in use or following pre-set schedules, like dimming lights in the evening.
Worker Productivity: These devices can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more complex work. For businesses, this translates to higher productivity and efficiency.
Health Monitoring: Wearable devices like smartwatches can track vital signs and send health data to medical teams, enabling faster responses to potential health issues.
Security Measures: Smart cameras and sensors allow for constant monitoring of homes or workplaces, sending alerts if unusual activity is detected.
Drawbacks of Smart Devices
Additional Costs: The initial cost of installing smart devices can be high, and ongoing maintenance can add to the expense.
Cyber Threats: The connectivity that makes smart devices so useful also makes them vulnerable to hacking. Without proper security measures, users risk cyberattacks.
Compatibility Issues: Devices from different brands may not work well together, limiting the effectiveness of a smart network.
Reliance on the Internet: Without a stable internet connection, many smart devices are rendered useless. This dependence can be a significant drawback in areas with limited or unreliable internet access.
Final Thoughts
Smart devices are an integral part of modern life, offering numerous benefits while also presenting some challenges. Understanding what makes a device smart—context awareness, autonomous computing, and connectivity—can help you make informed decisions about incorporating these technologies into your life. Whether enhancing productivity, saving energy, or improving security, smart devices have the potential to transform the way we live and work. However, it’s essential to consider the potential downsides, such as costs, security risks, and compatibility issues, to ensure you’re making the most of these innovative tools.
Technology
Can smart technology unlock a sustainable future?
Published
1 year agoon
August 19, 2024By
Mona Rossy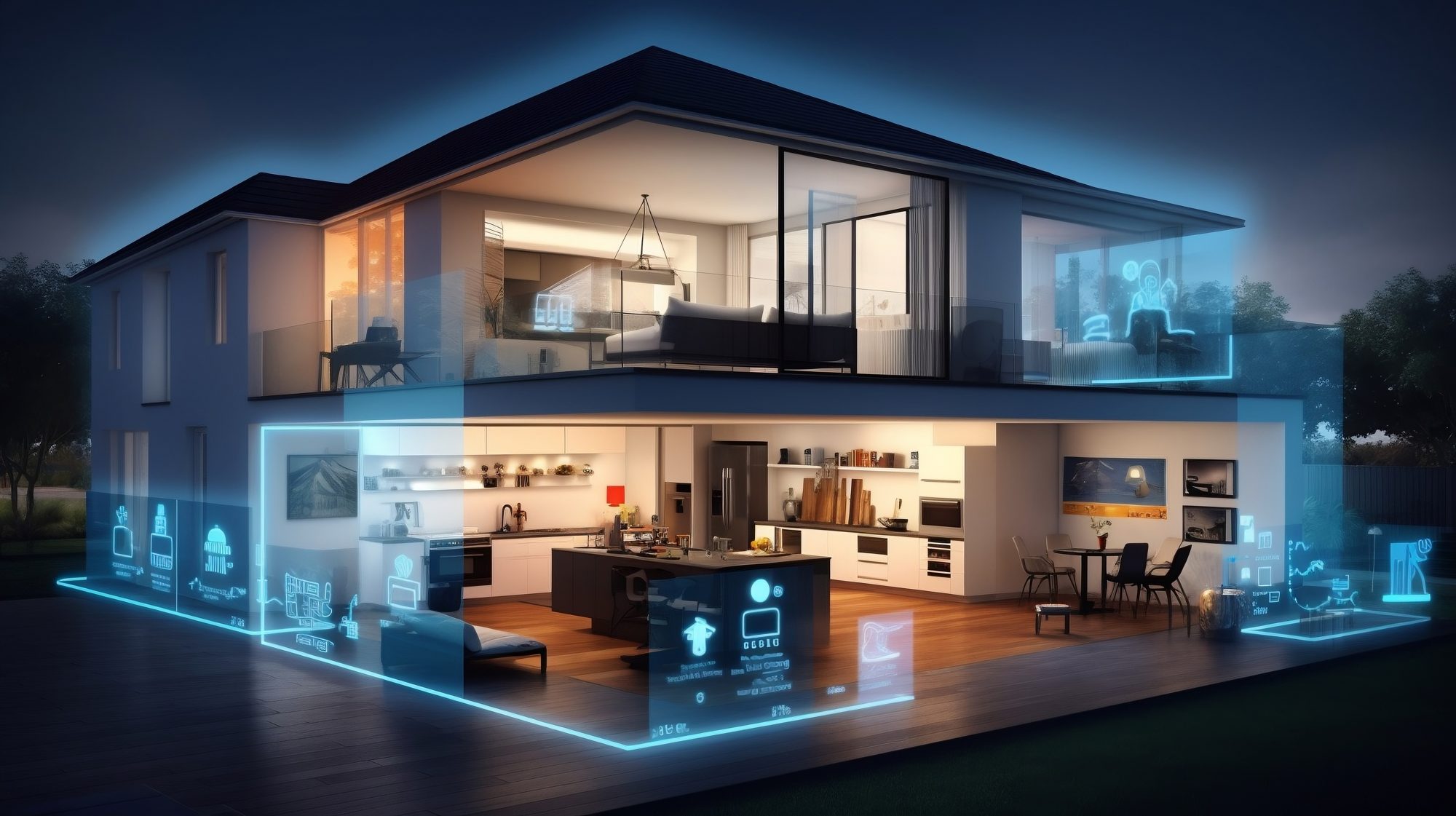
As energy costs soar across Europe, the drive for smarter, more sustainable living solutions has never been more urgent. Homeowners are now seeking ways to not only reduce their energy bills but also enhance their carbon footprint. The key to achieving this lies in integrating cutting-edge smart technology with innovative home solutions that prioritize ease of use, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
The transformation of industrial systems towards digitalization and decarbonization is mirrored in the residential sector. With the help of smart technology that enables them to live more sustainably, this shift heralds the emergence of connected communities where environmentally conscious residents strive to maximize their use of self-generated energy.
The Rise of Smart Communities
The fusion of top-down initiatives, like smart city projects, and grassroots movements spearheaded by tech-savvy communities is a new trend that is changing how we think about energy-efficient living. Particularly in Europe, this fusion is creating a fresh vision for the future of energy-efficient communities, where sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and convenience come together.
However, achieving this balance comes with challenges. The growing demand for domestic infrastructure, from heat pumps to electric vehicles, and the increasing reliance on 5G technology are transforming consumer behaviors. Effective tracking and sharing of energy data are now critical to managing these demands.
This article explores how communities are lowering their carbon footprints and energy costs through energy sharing and smart management. We’ll also delve into how smart technologies are revolutionizing everything from household appliances to security systems, and highlight a pioneering community near Stockholm that offers a blueprint for integrated, eco-friendly living.
Sustainable Living, Simplified
The COVID-19 pandemic fast-tracked changes in how we interact with our living spaces. Touch-free interfaces, once a novelty, have become standard in many buildings for enhanced hygiene. Meanwhile, smart solutions like intelligent lighting, heating, and HVAC systems are improving comfort and efficiency in both residential and commercial spaces.
For homeowners, these innovations offer more than just convenience. They help reduce energy bills, meet the growing demand for flexibility, and significantly lower the carbon footprint of buildings—crucial, given that buildings account for around 40% of global energy consumption.
In Sweden, a groundbreaking project involving ABB Smart Buildings, Samsung SmartThings, and other partners exemplifies how industry collaboration can drive the development of energy-efficient technologies. The Brobyholm community, in particular, is setting a new standard for smart living. Residents here are among the first in the world to benefit from a fully integrated smart home system that manages everything from energy consumption to security, all through a single mobile app.
Brobyholm: A Vision for the Future
Brobyholm represents a bold step toward a sustainable future. This new housing development aims to create a carbon-free community of 500, eventually expanding to 2,000 homes. Here, residents can make significant energy and carbon savings through enhanced access to connected smart home technology.
At the heart of Brobyholm is ABB’s InSite energy management system, which optimizes energy flows by monitoring and controlling key electrical assets, including photovoltaic (PV) generation, electric vehicle (EV) charging, and water and gas usage. This system ensures that energy is used efficiently, with excess power shared across the community or sold on the flexibility market, generating income for residents.
This approach not only reduces costs but also empowers residents to live sustainably. For example, surplus solar energy can be used to heat water tanks, while low solar output triggers energy-saving modes across devices. The inclusion of ABB Terra AC chargers for EVs further enhances energy optimization through vehicle-to-everything technology.
The Smart Homes of Tomorrow
The transition to net-zero living requires collaboration across industries and communities. Projects like Brobyholm demonstrate how open technology, industry standards, and partnerships can drive innovation and create sustainable living solutions.
As global energy demand rises, Brobyholm stands as an inspiring model of future-proof living, combining cutting-edge technology with a commitment to environmental responsibility. This community is not just a glimpse into the future; it’s a significant step toward a more sustainable, energy-efficient world.
Technology
New Revolution in MENA Region: FAST and Ad-Supported
Published
2 years agoon
December 27, 2023
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region has long been a hub of innovation and growth, and its streaming industry is no exception. The landscape has witnessed a significant shift in recent years, with the rise of flexible streaming services transforming how people consume content.
The convergence of advanced broadcast technology and widespread high-speed internet has paved the way for this streaming revolution, offering viewers many choices beyond traditional playout models.
The Rise of On-Demand Streaming
Over the past decade, on-demand streaming has seen unprecedented success in the MENA region. Projections suggest that by 2027, the region will boast over 36 million subscription video on-demand (SVOD) subscriptions.
While subscription platforms have firmly established themselves in the market, consumer expectations have evolved, giving rise to the trend of ad-supported content.

Ad-Supported Content: Meeting Viewer Demands
Ad-supported content has become a dynamic trend, meeting viewers’ demands for cost-effectiveness and personalized viewing experiences. The appeal lies in accessing an expansive content library without a financial commitment and in the ability to indulge in shows and movies tailored to individual interests.
Ad-supported video on demand (AVOD) has been a popular choice, but as preferences shift towards interest-based content, Free Ad-Supported Television (FAST) channels are gaining rapid favor.
These channels offer a unique platform for immersive experiences, allowing users to customize their viewing experiences by pausing, rewinding, and fast-forwarding through content.
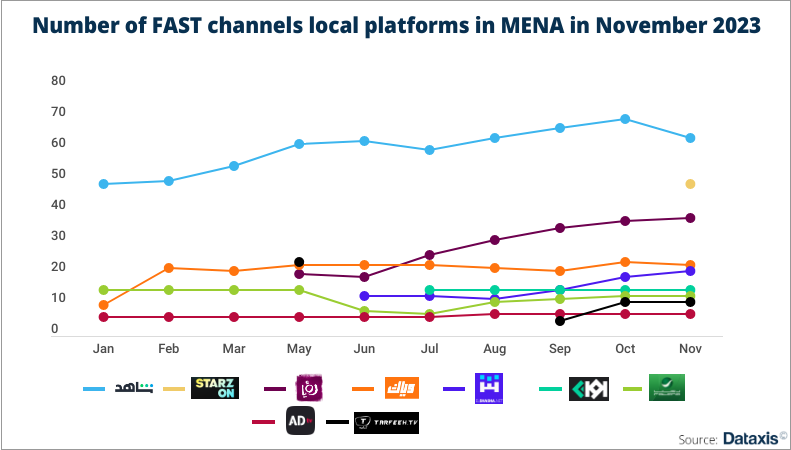
Exploring the FAST Channels
FAST channels represent a departure from familiar viewing models, combining the advantages of linear TV with the flexibility of on-demand streaming.
They empower consumers to have greater control over their viewing experiences, offering a curated selection of localized and globally popular content, including live TV.
In the MENA region, where cultural diversity is significant, resonating with audiences is crucial. FAST channels cater to this by providing a curated selection of content that appeals to a broad audience without the constraints of a subscription model.
Digital Investment and Monetization
Digital advertising has seen a marked increase globally, and the MENA region is no exception. FAST channels have become avenues for reaching wider audiences, resulting in a boost in revenue streams.
Despite offering free content, these channels attract a diverse and engaged audience, giving brands a unique opportunity to showcase their products or services.
The FAST model revolutionizes the advertising experience by allowing advertisers to adjust their campaigns in real-time dynamically. This flexibility ensures that advertising messages adapt to changing circumstances, reaching the right viewers at the right time.
Data-driven targeting techniques enable advertisers to pinpoint specific audience segments based on interests, behavior, and demographics, creating highly personalized and relevant ads that enhance engagement.

Navigating Technological Requirements
While the monetization prospects from FAST channels are promising, it’s crucial not to overlook the associated technological requirements. The unique business model of FAST TV channels, which relies on ad sales revenue, demands a deep understanding of channel management and ad sales operations.
Proficiency in content licensing and compliance is equally crucial due to various regions’ different advertising and broadcasting regulations.
As the MENA region stands poised to lead the FAST race, improving connectivity will provide new opportunities for channel providers to reach larger audiences across a spectrum of devices.
The coming times promise closer collaboration between broadcasters and advertisers, paving the way for innovative viewing solutions tailored to a thriving young demographic.

Leading Platforms in the MENA Streaming Landscape
Several platforms are leading the charge in the MENA streaming landscape, offering diverse content to cater to evolving viewer preferences.
Awaan: Gateway to Rich Arabic Content
Awaan serves as the Arab world’s gateway to entertainment, offering diverse shows, movies, and exclusive content that caters to locally relevant and globally appealing entertainment.
Weyyak: Global Stage for Arabic Content
Weyyak provides a global stage for Arabic content, specializing in Arabic dramas and series, with an extensive library of culturally resonant content.
Shahid: Premium Content Bridging Cultures
Shahid seamlessly bridges cultures through its vast collection of Arabic and international shows, catering to diverse tastes and ensuring viewers find an eclectic mix of entertainment options.
OSN Play: Beyond Traditional Boundaries
OSN Play goes beyond traditional entertainment boundaries by offering a blend of live TV, on-demand content, and exclusive programming, making it a preferred choice for those seeking variety and quality.
StarzPlay Arabia: Home of Blockbuster Entertainment
StarzPlay Arabia has become synonymous with blockbuster entertainment in the Middle East, boasting an extensive library of movies, series, and exclusive Starz content.
Tarfeeh: Redefining Entertainment Accessibility
Tarfeeh channels contribute to the vibrant tapestry of streaming choices, redefining entertainment accessibility in the MENA region with a commitment to offering diverse content and a unique viewing experience.
Dreamax: Gateway to Diverse Content
Dreamax stands out as a gateway to diverse content, catering to the evolving preferences of Middle Eastern audiences by providing a seamless streaming experience and a curated selection of shows.

Future Outlook
As the streaming landscape in the Middle East continues to evolve, these platforms are at the forefront of providing innovative solutions for a thriving young demographic.
With better connectivity enveloping the region, viewers can expect an even broader range of entertainment options delivered seamlessly across various devices.
In conclusion, the MENA streaming scene is witnessing a transformative era, and platforms like Awaan, Weyyak, Shahid, OSN Play, StarzPlay Arabia, Tarfeeh, and Dreamax are not just streaming services but cultural hubs that cater to the rich tapestry of preferences in the Middle East.
As these platforms redefine the digital entertainment experience, viewers can look forward to a future where streaming is not just a trend but a way of life.
The advent of FAST channels adds a new dimension to this journey, giving viewers more control and flexibility in their content consumption.
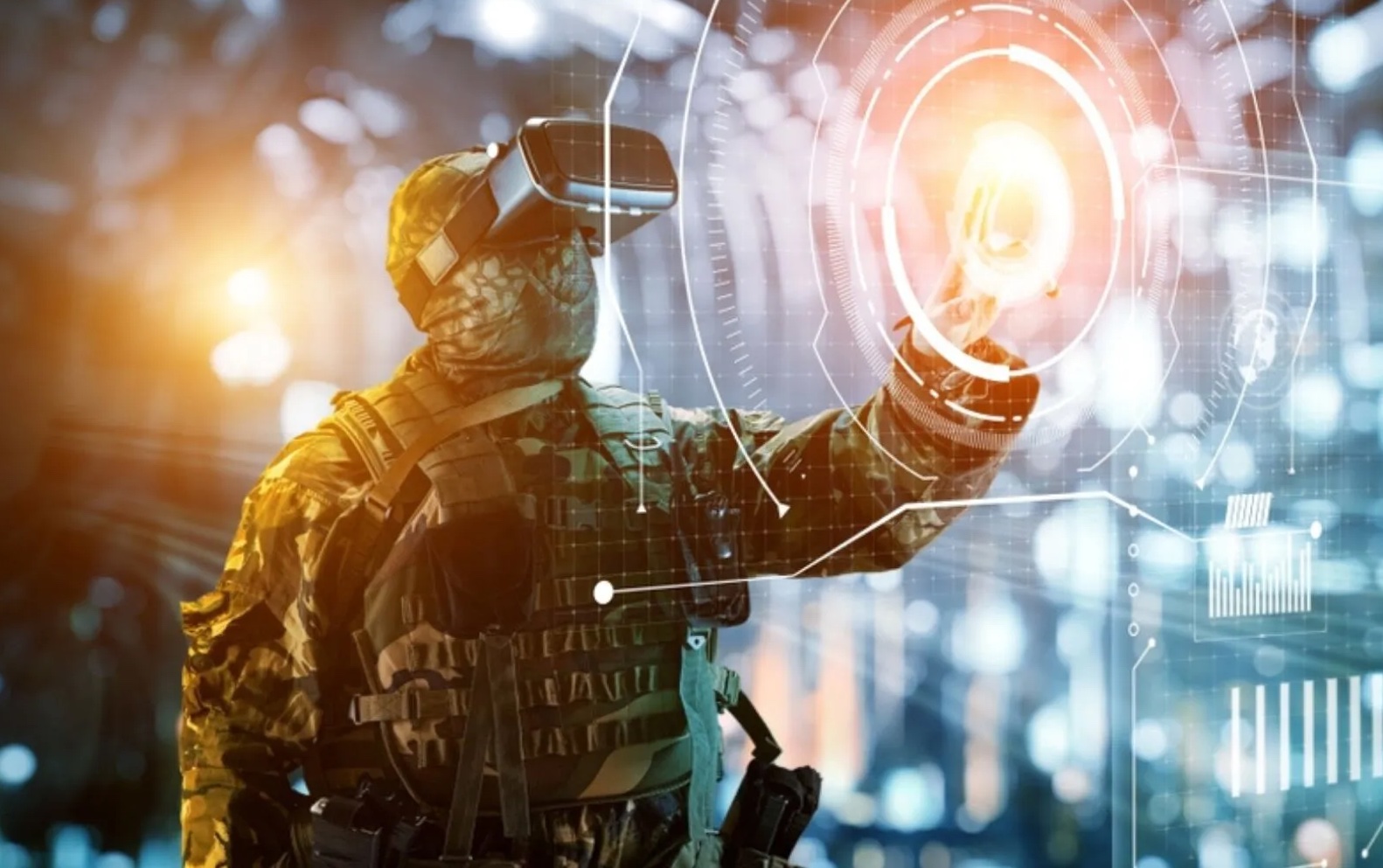

Due to the unstoppable march of technological advancements, the face of warfare has undergone a significant transformation in recent decades. From the unmanned aerial vehicles that dominate the skies to the artificial intelligence that guides our weaponry, technology has permeated every aspect of modern combat, fundamentally altering how wars are fought and won.
The Proliferation of Unmanned Systems
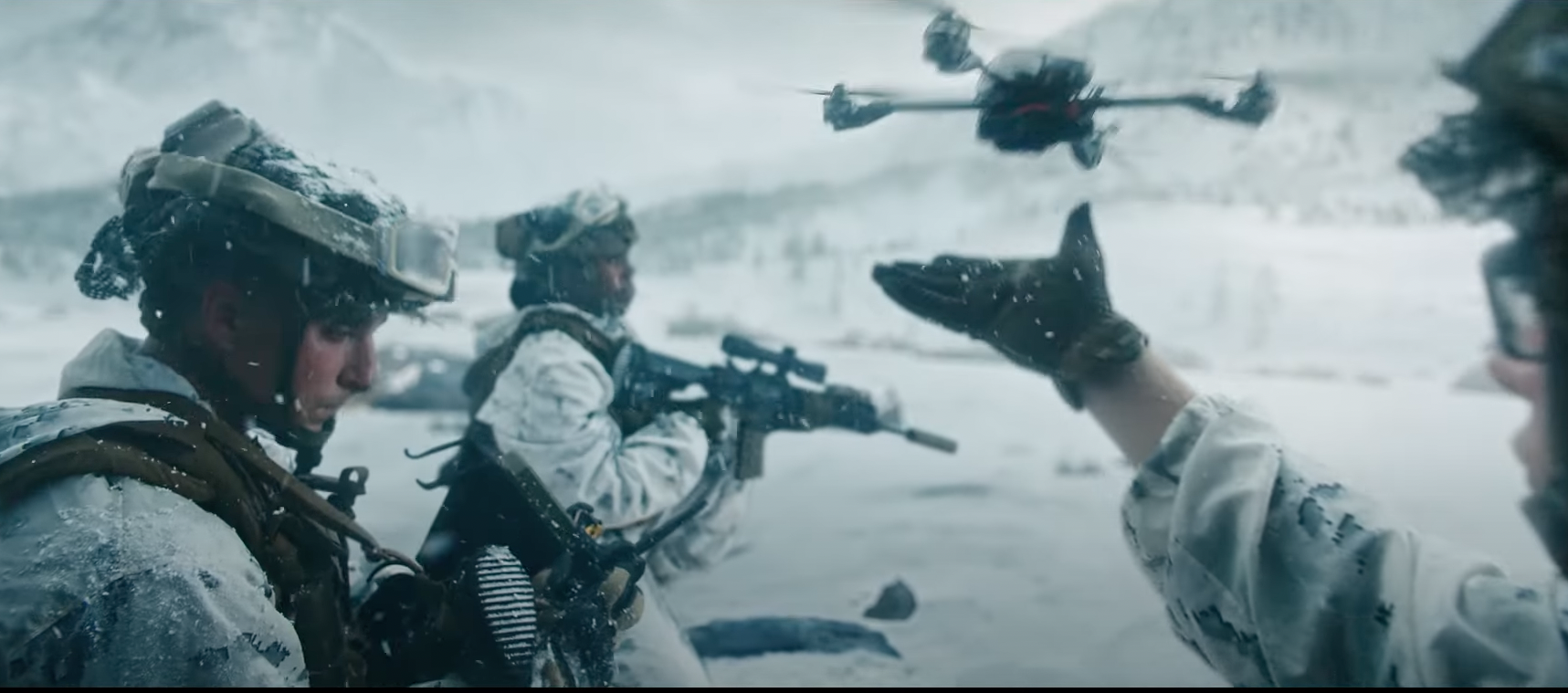
One of the most transformative technologies to emerge in modern warfare is the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), more commonly known as a drone. These unmanned aircraft have revolutionized warfare by providing a means of conducting surveillance, reconnaissance, and even combat missions without risking the lives of human pilots.
Their ability to operate in hazardous environments, collect real-time data, and strike targets precisely has made them indispensable tools for militaries worldwide.
The use of drones has not been without its ethical and legal challenges. Concerns over civilian casualties and the potential for autonomous weapons systems to operate without human oversight have sparked debate about the proper role of drones in warfare. Despite these challenges, the proliferation of drones is likely to continue, further blurring the lines between war and peace.

AI: Revolutionizing Strategic Planning and Weaponry
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as another game-changer in modern warfare. Its ability to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions has transformed strategic planning, enabling militaries to gain a deeper understanding of the battlefield and make more informed decisions.
AI is also being integrated into weapon systems, enhancing their precision and effectiveness. For instance, AI-powered missile systems can identify and track targets more accurately, reducing the risk of misfires.
However, the integration of AI in warfare raises significant ethical concerns. The potential for autonomous weapons systems to operate without human oversight raises questions about losing human control over warfare and the potential for unintended consequences. Governments and militaries must carefully consider the ethical implications of AI in warfare to ensure that it is used responsibly and ethically.

Cyber Warfare
The advent of the digital age has ushered in a new dimension of warfare: cyber warfare. This conflict involves using technology to disrupt or destroy an enemy’s computer systems, networks, and digital infrastructure.
Cyberwarfare has the potential to cripple a nation’s defense capabilities, disrupt its economy, and cause widespread chaos.
The growing sophistication of cyberwarfare capabilities has made it an increasingly prominent threat in modern warfare. As militaries become more reliant on interconnected technology, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. This has led to a growing emphasis on cyber defense, with militaries investing heavily in cyber security measures to protect their systems and data.
The Lifeline of Modern Warfare
Communication technology has also seen significant advancements in recent decades, with secure and encrypted communication systems now being a standard feature in military operations. These systems allow for efficient coordination and information sharing among different units, enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness.
The importance of reliable and secure communication in modern warfare cannot be overstated. Effective communication is crucial for command and control, battlefield coordination, and intelligence sharing. Without secure communication, militaries would be severely hampered in their ability to conduct operations effectively.

Ethical Considerations
The transformative impact of technology on modern warfare has not come without ethical challenges. Using unmanned systems, autonomous weapons, and cyber warfare raises concerns about the loss of human control over warfare, the potential for collateral damage, and the blurring of the lines between war and peace.
As technology evolves at an unprecedented pace, engaging in ongoing discussions about the ethical implications of its use in warfare is essential. Governments, militaries, and civil society must work together to establish clear guidelines and regulations that ensure that technology is used responsibly and ethically in pursuing peaceful resolutions to conflicts.
Technological advancements will probably shape warfare more and more in the future. New technologies, such as quantum computing and hypersonic weapons, can potentially revolutionize the way wars are fought further. It is, therefore, crucial to anticipate and prepare for these emerging threats, ensuring that militaries can adapt to new technologies while upholding ethical and legal principles.
Technology has played a pivotal role in modern warfare, transforming every aspect of combat, from intelligence gathering to strategic planning to operational execution.
This transformative impact, however, has come with ethical and legal challenges, highlighting the need for ongoing discussions about the responsible and ethical use of technology in warfare.
As technology evolves, militaries must adapt while upholding ethical principles to ensure that warfare is conducted to minimize harm and promote peace.
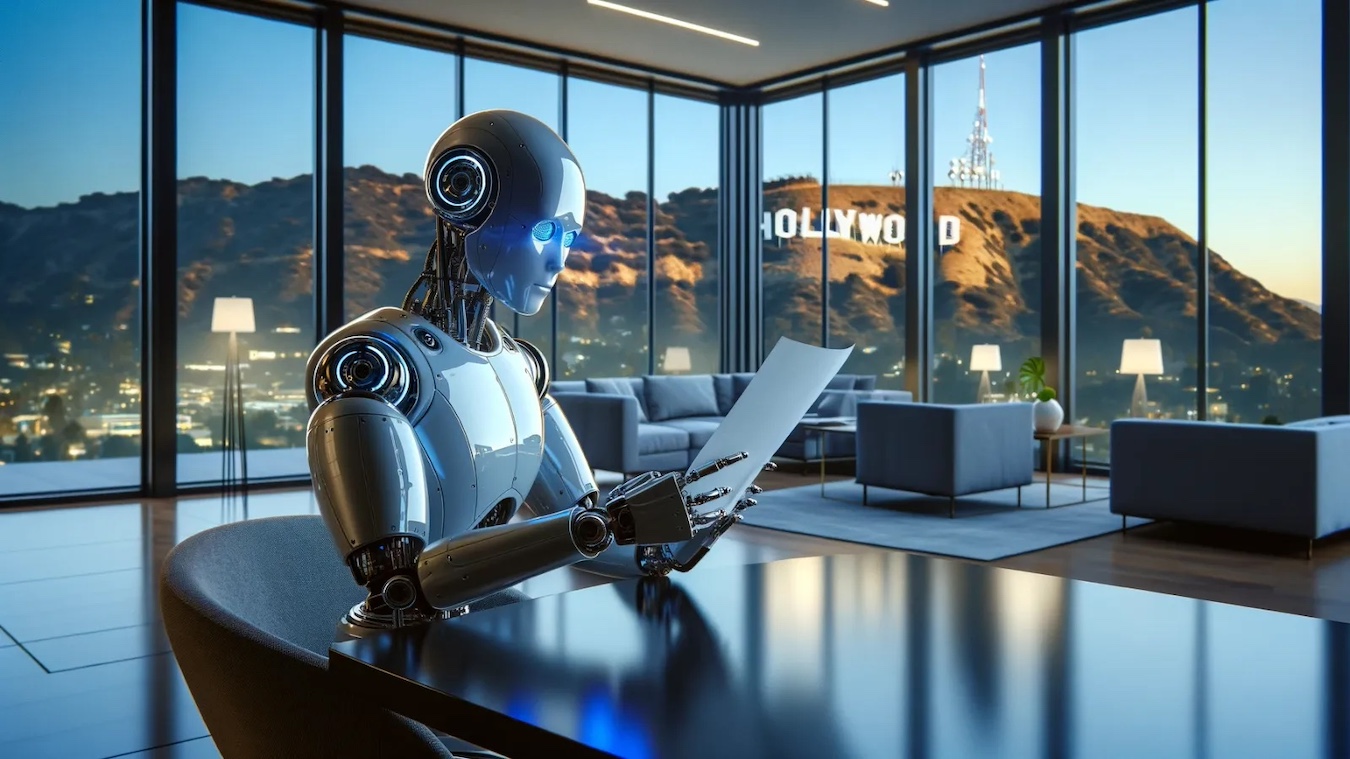

Imagine a future not too distant, the year 2025, where the glittering lights of the Academy Awards illuminate a groundbreaking moment in cinematic history: an artificial intelligence (AI) system clinches the Oscar for Best Original Screenplay.
This is no sci-fi fantasy; it’s a rapidly approaching reality where AI’s foray into filmmaking is not just a possibility but an imminent revolution.
AI’s Evolution in Storytelling
The art of storytelling, an intrinsic part of human culture dating back 30,000 years to cave drawings in France, is undergoing a seismic shift. The narrative journey has evolved from hand-illustrated cave walls to pen and paper and now to the realm of digital technology, where stories are visually narrated through movies.
AI, in its ever-advancing form, is set to take the helm of this evolution. Renowned figures like Joe Russo, director of Marvel’s “Avengers: Endgame” and an AI company board member, affirm this progression. They foresee AI radically altering the way we conceive and tell stories.
AI emerges as a game-changing ally in Hollywood, where time, effort, and financial investment are crucial. It’s not just about generating scenes, scripts, characters, dialogues, and soundtracks; AI’s role extends to analyzing scripts for their box office potential, suggesting the viability of projects, and even scouting film locations.
Director Chad Nelson’s use of AI to produce an animated short film vividly demonstrates this technological prowess by showcasing AI’s capacity to produce thousands of images and contribute creatively to filmmaking.
The Magic of AI
AI’s capabilities in film extend beyond mere logistical and creative support. It breathes new life into cinema through enhancements like de-aging actors, exemplified by Harrison Ford’s rejuvenated appearance in the new Indiana Jones film.
Greg Brockman, president of OpenAI, envisions a future where AI transcends traditional viewing experiences, offering personalized movies tailored to individual tastes. Imagine coming home, weary from work, and asking your AI to whip up a light-hearted romcom set in Greece, with you as the protagonist alongside Marilyn Monroe.
It’s a future where the line between viewer and participant blurs, creating a uniquely immersive experience.

The Limitations of AI in Creativity
Despite these advancements, AI’s infiltration into the creative domain isn’t without its challenges. The essence of storytelling, deeply rooted in human emotion and interaction, remains a frontier AI struggles to conquer fully.
Director John Finger and AI expert Stuart Russell point out that AI, in its current form, operates with a level of objectivity that lacks the nuanced understanding of the human condition necessary for compelling storytelling.
AI-generated art, they argue, is only as good as the human input guiding it, highlighting the collaborative nature of this technological tool.
The Future of AI in Filmmaking
As we navigate this new era of AI-driven cinema, the question arises: will AI replace human creatives, or will it serve as a collaborative tool that enhances human creativity? The potential of AI to perform tasks with speed and efficiency that humans can’t match is undeniable.
However, its ability to fully grasp and replicate the depth of human emotion and creativity remains debatable. The journey of AI in filmmaking is not just about technological prowess; it’s a dialogue between machine efficiency and human creativity.

AI and Human Creativity
As we approach 2025, the future of filmmaking is a landscape where AI plays a pivotal role, yet it’s a domain still deeply rooted in human creativity and emotion. As AI continues to evolve and expand its capabilities, the film industry stands on the cusp of a new era.
One where AI is not just a tool but a collaborator, augmenting human imagination and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in storytelling.
This partnership between humans and machines promises a cinematic future as exciting as it is uncertain, beckoning us to embrace both the possibilities and challenges it brings.
Technology
Don’t Get Fooled Online: Beat Social Engineering Scams
Published
2 years agoon
December 11, 2023By
Samy Deyyab
Just like in a real neighborhood, keeping our online streets safe is super important. Today, let’s chat about something called social engineering – a tricky way bad guys try to trick us online. Imagine someone pretending to be your friend to get your secret cookie recipe; that’s what social engineering is in the cyber world.
What’s Social Engineering Anyway?
Let’s break it down. Social engineering is like a con artist’s trick but in the digital world. It’s when someone uses mind games to get you to share private information, like your passwords or bank details. They might pretend to be someone you trust, like a bank or a company, and ask for your details. Or they might scare you into thinking something’s wrong and that you must give them information to fix it.

The Tricks They Use
Here are some sneaky ways these tricksters operate:
- Phishing: Ever get an email that looks like it’s from a real company, but something feels off? That’s phishing. They’re fishing for your information with a fake email.
- Spear Phishing: This is like phishing but more targeted. Imagine getting an email that knows a bit about you – it’s creepy and more convincing.
- Pretexting: Here, the bad guys invent a whole story. They might pretend to be from tech support and say they need your password to fix your computer.
- Baiting: It’s like dangling a carrot. They promise you something cool, like free music downloads, but they get your personal information when you bite.
How to Spot the Bad Guys
Even though these tricks can be clever, there are ways to spot them:
- Too Much Drama: If an email or message makes you feel super worried or rushed, take a breath. It might be a trick.
- Who’s This?: Got a message from someone you don’t know? Be cautious, especially if they’re asking for personal info.
- Oops, That’s a Typo: Official emails usually don’t have silly spelling mistakes. If you see some, that’s a red flag.
- That Doesn’t Look Right: Trust your gut if an email’s logo or website address looks weird. It’s probably fake.

Keeping Safe: Your Cyber Shield
Here’s how to keep yourself safe:
- Think Before You Click: Don’t rush. If something feels off, it probably is.
- Double-Check: If unsure, call the company or check their official website. Better safe than sorry!
- Be Link Smart: Hover your mouse over a link to see where it really goes. If it looks fishy, don’t click!
- Update Your Security: Keep your computer’s antivirus and software up to date. It’s like having a good lock on your front door.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest tricks so you know what to look out for.
Be a Cyber Smarty
Remember, social engineering is all about tricking you, but you’re smarter than them. Knowing their tricks, looking out for the warning signs, and being a little skeptical, you can keep your digital self safe. Let’s keep our online neighborhood friendly and secure by being alert and informed. Stay safe out there!

Fenikss Casino: Kā Veikt Reģistrāciju un Pirmo Iemaksu
Slottyway PL Nowoczesne kasyno online dla polskich graczy

Unlocking the Power of Smart Devices: What You Need to Know

Is a New Era of United States-China Space Collaboration Possible?

Can smart technology unlock a sustainable future?

Start Your Day Right: The Benefits of a Clutter-Free Desk

Emerging Titan: India’s Strategic Move on The Global Chessboard

Use these services to get free cloud space

From Unity to Split: Is This Libya’s New Chapter?

New Revolution in MENA Region: FAST and Ad-Supported

Navigating The New Silk Road: A Ten-Year Retrospective

How Technology is Reshaping Modern Warfare
Trending
-

 Poltics2 years ago
Poltics2 years agoEmerging Titan: India’s Strategic Move on The Global Chessboard
-

 Technology3 years ago
Technology3 years agoUse these services to get free cloud space
-

 Poltics2 years ago
Poltics2 years agoFrom Unity to Split: Is This Libya’s New Chapter?
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoNew Revolution in MENA Region: FAST and Ad-Supported
-

 Poltics2 years ago
Poltics2 years agoNavigating The New Silk Road: A Ten-Year Retrospective
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoHow Technology is Reshaping Modern Warfare


